Examples¶
When setting up a new project with the Project Wizard it will come with a set of example to learn the usage of the simulation environment.
All following examples will execute a simple sine movement by moving the L1 and L2 joints of the robot. You can sart the examples by opening the world files worlds/Example... in your project created by the Project Wizard. (Start Webots -> Open World)
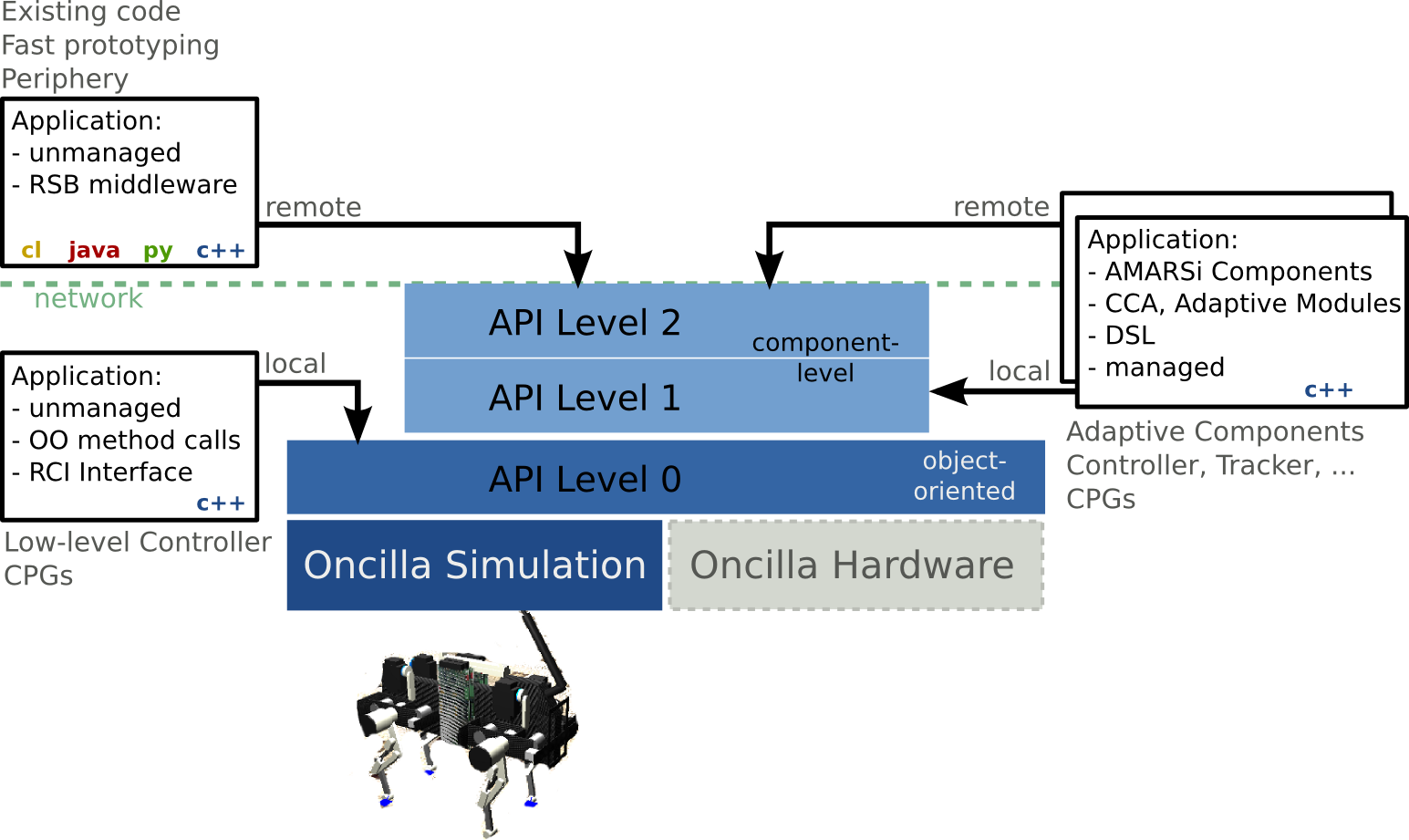
The examples should be properly set up and compiled by the Project Wizard, and should all perform the same movement, but use different API levels of the Oncilla:
- API Level 0 is an C++ API defined by liboncilla, that provides direct access to sensor values and sending command to the actuators. See Example 1 below.
- API Level 1 is defined in libcca-oncilla and provides local component-level access by using the AMARSi Component Architecture CCA. Applications are implemented as reusable CCA components that can be combined to more complex systems and are managed by the framework. See Example 2 below for an example component.
- API Level 2 is similar to API Level 1 and also defined in libcca-oncilla . It provides the same access as API Level 1, but opens a remote interface by facilitating the middleware RSB (Robotics Service Bus). This API level can be used by CCA component remotely over the network (running on different machines) and by arbitrary C++, Java and Python applications using RSB. See Example 3 for a Python application. It also allows usage of the RSB tools like RSBag for recording and replaying movements, see Example 4.
Example 1: Simple Sine Movement¶
You should see the robot performing a simple walking movement, which is not a necessarily meaningful walking gate. ;)
For more information on the example and how to change and extend it, see Simple Sine Movement.
Example 2: Simple Sine Movement Component¶
The second example will do exactly the same as Example 1, but is written as a CCA component and therefore ready for usage in the AMARSi Software Architecture.
For more information on the example and how to change and extend it, see Simple Sine Movement Component.
Example 3: External Components / Streaming¶
The third example will open a remote interface (API Level 2) and waits for commands from external applications, scripts or tools. To show the openness of the interface, the same movement as above is implemented as a Python Script, that communicates with the Simulator over the middleware RSB (Robotics Service Bus).
For more information on the example and how to change and extend it, see Python Simple Sine Movement.
Example 4: Recording and Replaying Movements¶
The fourth example replays a previously recorded movement over the middleware RSB (Robotics Service Bus) by using RSBag Tools.
For more information on the example and how to change and extend it, see Replaying Simple Sine Movement.