 |
Image Component Library (ICL)
|
 |
Image Component Library (ICL)
|
Applies Gabor filter operation on images. More...
#include <GaborOp.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| GaborOp () | |
| creates an empty GaborOp | |
| GaborOp (const utils::Size &kernelSize, std::vector< icl32f > lambdas, std::vector< icl32f > thetas, std::vector< icl32f > psis, std::vector< icl32f > sigmas, std::vector< icl32f > gammas) | |
| creates a new gabor op with given kernel size and parameters | |
| ~GaborOp () | |
| void | setKernelSize (const utils::Size &size) |
| sets the current kernel size | |
| void | addLambda (float lambda) |
| add a new lambda value | |
| void | addTheta (float theta) |
| add a new theta value | |
| void | addPsi (float psi) |
| add a new psi value | |
| void | addSigma (float sigma) |
| add a new sigma value | |
| void | addGamma (float gamma) |
| add a new gamma value | |
| void | updateKernels () |
| update the current kernels by currently possible value combinations | |
| virtual void | apply (const core::ImgBase *poSrc, core::ImgBase **ppoDst) |
| apply all filters to an image | |
| std::vector< icl32f > | apply (const core::ImgBase *poSrc, const utils::Point &p) |
| apply all filters to an image at a specific position | |
| const std::vector< core::Img32f > & | getKernels () const |
| returns all currently created kernels | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static core::Img32f * | createKernel (const utils::Size &size, float lambda, float theta, float psi, float sigma, float gamma) |
| static function to create a gabor kernel by given gabor parameters | |
Private Attributes | |
| std::vector< icl32f > | m_vecLambdas |
| std::vector< icl32f > | m_vecThetas |
| std::vector< icl32f > | m_vecPsis |
| std::vector< icl32f > | m_vecSigmas |
| std::vector< icl32f > | m_vecGammas |
| std::vector< core::Img32f > | m_vecKernels |
| std::vector< core::ImgBase * > | m_vecResults |
| utils::Size | m_oKernelSize |
Applies Gabor filter operation on images.
A short introduction to Gabor filters can be found at Wikipedia: A Gabor filter is a linear filter whose impulse response is defined by a harmonic function multiplied by a Gaussian function. Because of the multiplication-convolution property, the Fourier transform of a Gabor filter's impulse response is the convolution of the Fourier transform of the harmonic function and the Fourier transform of the Gaussian function.
![\[ g(x,y;\lambda,\theta,\psi,\sigma,\gamma)=\exp(-\frac{x'^2+\gamma^2y'^2}{2\sigma^2})\cos(2\pi\frac{x'}{\lambda}+\psi) \]](form_89.png)
where
![\[ x' = x \cos\theta + y \sin\theta\, \]](form_90.png)
and
![\[ y' = -x \sin\theta + y \cos\theta\, \]](form_91.png)
In this equation, 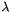 represents the wavelength of the cosine factor,
represents the wavelength of the cosine factor, 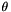 represents the orientation of the normal to the parallel stripes of a Gabor function in degrees,
represents the orientation of the normal to the parallel stripes of a Gabor function in degrees, 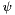 is the phase offset in degrees, and
is the phase offset in degrees, and 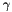 is the spatial aspect ratio, and specifies the ellipticity of the support of the Gabor function.
is the spatial aspect ratio, and specifies the ellipticity of the support of the Gabor function.
Gabor filters are directly related to Gabor wavelets, since they can be designed for number of dilations and rotations. However, in general, expansion is not applied for Gabor wavelets, since this requires computation of biorthogonal wavelets, which may be very time-consuming. Therefore, usually, a filter bank consisting of Gabor filters with various scales and rotations is created. The filters are convolved with the signal, resulting in a so-called Gabor space. This process is closely related to processes in the primary visual cortex. The Gabor space is very useful in e.g., image processing applications such as iris recognition. Relations between activations for a specific spatial location are very distinctive between objects in an image. Furthermore, important activations can be extracted from the Gabor space in order to create a sparse object representation (cite http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gabor_filter).
The GaborOp class provides basic functionalities for applying Gabor filters on Images. To achieve optimal performance, it wraps the ConvolutionOp class to realize the internal image convolution operations. Determined by a set op input parameters, it internally creates a filter bank that caches all gabor masks. In contrast to other filters, it knows two modes:
The GaborOp class provides functionalities for the creation of Gabor-Filter kernels, as well as for applying gabor filter operation on images. As mentioned above, in contrast to other convolution operations, Gabor filters are often applied as so called Gabor-Jets at some specified image locations only. A Gabor-Jet complies a stack of gabor kernels that are created by some methodical variation of one, some or all gabor mask parameters.
Each GaborOp object provide function to create a gabor jet internally, whereas in the easiest case, there is only one value for each parameter, an consequently, only a single gabor mask is created.
In addition to the parameters mentioned in the formula above, the size of the created gabor kernels must be set, and the parameter values must be adapted to to it. In the following, each parameter is explained again, but this time with respect to its underlying effect for a kernel size of KWxKH.
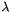 wave length of pixels (e.g. if set to KW, the wave will oscillate exactly once for direction (
wave length of pixels (e.g. if set to KW, the wave will oscillate exactly once for direction ( 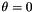 )
)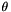 orientation of the wave (0-> wave direction is 3 o'clock,
orientation of the wave (0-> wave direction is 3 o'clock, 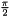 -> wave direction is 12 o'clock)
-> wave direction is 12 o'clock)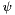 phase shift of the wave
phase shift of the wave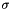 std.deviation of the Gaussian multiplied with the wave (in pixels)
std.deviation of the Gaussian multiplied with the wave (in pixels)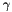 aspect-ratio of the Gaussian
aspect-ratio of the Gaussian creates an empty GaborOp
| icl::filter::GaborOp::GaborOp | ( | const utils::Size & | kernelSize, |
| std::vector< icl32f > | lambdas, | ||
| std::vector< icl32f > | thetas, | ||
| std::vector< icl32f > | psis, | ||
| std::vector< icl32f > | sigmas, | ||
| std::vector< icl32f > | gammas | ||
| ) |
creates a new gabor op with given kernel size and parameters
The Gabor-Jet internally created consist of one convolution kernel for each possible combination of the parameter values. E.g. if the parameters are:
the gabor jet consist of 4 convolution kernels with fixed params 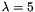 ,
, 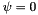 ,
, 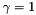 and variable params
and variable params
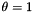 and
and 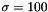
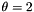 and
and 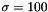
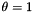 and
and 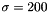
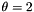 and
and 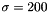
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::addGamma | ( | float | gamma | ) |
add a new gamma value
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::addLambda | ( | float | lambda | ) |
add a new lambda value
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::addPsi | ( | float | psi | ) |
add a new psi value
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::addSigma | ( | float | sigma | ) |
add a new sigma value
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::addTheta | ( | float | theta | ) |
add a new theta value
| virtual void icl::filter::GaborOp::apply | ( | const core::ImgBase * | poSrc, |
| core::ImgBase ** | ppoDst | ||
| ) | [virtual] |
apply all filters to an image
The output image gets as many channels as kernels could be created by combining given parameters. Channels c of ppoDst is complies the convolution result of the c-th kernel.
Implements icl::filter::UnaryOp.
| std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::apply | ( | const core::ImgBase * | poSrc, |
| const utils::Point & | p | ||
| ) |
apply all filters to an image at a specific position
The result vector contains the filter-response for all kernels
| static core::Img32f* icl::filter::GaborOp::createKernel | ( | const utils::Size & | size, |
| float | lambda, | ||
| float | theta, | ||
| float | psi, | ||
| float | sigma, | ||
| float | gamma | ||
| ) | [static] |
static function to create a gabor kernel by given gabor parameters
As reminder:
![\[ g(x,y;\lambda,\theta,\psi,\sigma,\gamma)=\exp(-\frac{x'^2+\gamma^2y'^2}{2\sigma^2})\cos(2\pi\frac{x'}{\lambda}+\psi) \]](form_89.png)
where
![\[ x' = x \cos\theta + y \sin\theta\, \]](form_90.png)
and
![\[ y' = -x \sin\theta + y \cos\theta\, \]](form_91.png)
| const std::vector<core::Img32f>& icl::filter::GaborOp::getKernels | ( | ) | const [inline] |
returns all currently created kernels
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::setKernelSize | ( | const utils::Size & | size | ) |
sets the current kernel size
if the kernels have already been created, they are updated to this new size value
| void icl::filter::GaborOp::updateKernels | ( | ) |
update the current kernels by currently possible value combinations
std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecGammas [private] |
std::vector<core::Img32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecKernels [private] |
std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecLambdas [private] |
std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecPsis [private] |
std::vector<core::ImgBase*> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecResults [private] |
std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecSigmas [private] |
std::vector<icl32f> icl::filter::GaborOp::m_vecThetas [private] |
 1.7.6.1
1.7.6.1